
How hybrid cars work – types, features & advantages over ICE cars
As fuel prices surge and air quality deteriorates across Indian cities, hybrid cars are emerging as the ideal middle ground between traditional petrol vehicles and full-electric cars. In this blog, we break down how hybrid vehicles work, their unique features, the different types available in India, and why they are a smarter choice over ICE cars for today’s urban drivers.
As fuel prices in India continue to rise and cities grapple with air pollution, hybrid cars have emerged as a powerful bridge between traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and fully electric vehicles (EVs). But how exactly do hybrid cars work? What makes them different from regular petrol or diesel vehicles? And are they really worth the investment?
In this blog, we will explore how hybrid cars work, the unique features they offer, the different types of hybrid systems available in India and how they compare with ICE vehicles.
What Is a Hybrid Car? A hybrid car is a vehicle that combines two power sources: a traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) and one or more electric motors powered by a battery. These systems work together or independently to deliver better fuel efficiency, lower emissions and a smoother driving experience, especially useful for Indian urban conditions with frequent stop-start traffic.
How Do Hybrid Cars Work? At the heart of a hybrid car is the ability to seamlessly switch between or combine the power of an engine and an electric motor based on driving conditions. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
Internal Combustion Engine: Powers the vehicle like a regular petrol/diesel car, especially at higher speeds or when more power is needed.
Electric Motor(s): Drives the vehicle in low-speed conditions or assists the engine during acceleration.
Battery Pack: Stores electrical energy for the motor. In most hybrids, the battery charges while driving, no need to plug it in.
Power Control Unit (PCU): Manages the flow of power between engine, motor and battery for optimal performance.
Regenerative Braking: Captures energy from braking and stores it back in the battery, enhancing efficiency in traffic-heavy Indian roads.
This intelligent balance helps reduce fuel consumption and emissions, especially in city driving, where hybrids often deliver over 20–26 km/l, compared to 12–16 km/l in conventional cars.
Features of Hybrid Cars That ICE Cars Don’t Have
Hybrid vehicles offer several exclusive features not found in conventional ICE vehicles:
- 1.
Regenerative Braking
Instead of wasting energy as heat during braking, hybrids capture and store that energy in the battery for later use, especially helpful in stop-and-go Indian traffic. - 2.
Electric-Only Drive Mode
At low speeds or in heavy traffic, hybrids can run purely on electric power, saving fuel and cutting emissions. - 3.
Automatic Start-Stop
The engine automatically turns off at stops (like traffic signals) and restarts when needed, saving fuel and reducing noise. - 4.
Battery-Assist Acceleration
Electric motors deliver instant torque, making acceleration smoother and quicker, great for overtaking on Indian roads. - 5.
Energy Monitoring Display
Many hybrids offer a visual dashboard that shows real-time energy flow between engine, battery and motor, encouraging efficient driving. - 6.
Lower Emissions
Hybrids emit fewer pollutants than ICE vehicles, making them suitable for meeting BS6 norms and qualifying for green incentives in some Indian states.
Types of Hybrid Cars Hybrid technology isn’t one-size-fits-all. Here are the main types, along with examples available or relevant to the Indian market:
- 1.
Full Hybrid (FHEV)
Can run on electric power alone, engine alone, or both combined.
 Example: Toyota Urban Cruiser Hyryder, Honda City e:HEV - 2.
Mild Hybrid (MHEV)
The electric motor assists the engine but can’t power the car alone.
 Example: Maruti Suzuki Ciaz Smart Hybrid, Maruti Brezza SHVS - 3.
Plug-in Hybrid (PHEV)
Can be recharged via an external power source and has a longer electric-only range (usually 40–60 km).
 Example: Volvo XC90 Recharge (Luxury segment) - 4.
Series Hybrid
Only the electric motor powers the wheels. The engine charges the battery.
 Rare in India, but some global models use this approach. - 5.
Parallel Hybrid
Both engine and motor are connected to the drivetrain and work together.
 Example: Older Honda Accord Hybrid - 6.
Series-Parallel Hybrid
Combines both series and parallel features, offering maximum efficiency and flexibility.
 Example: Toyota Camry Hybrid
**Hybrid Cars vs ICE Cars: What’s the Difference?
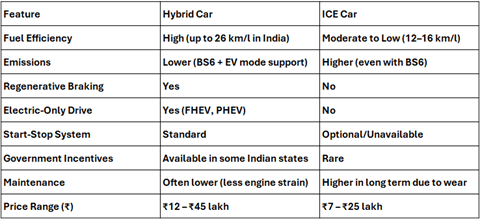
Advantages of Hybrid Cars
Fuel Savings Hybrid cars can reduce your fuel bill by 30–50%, depending on the model and your driving habits. With petrol prices around ₹100/litre, that’s a big saving in the long run.
Environmental Benefits Reduced greenhouse gas emissions help improve urban air quality, essential for Indian cities facing rising AQI levels.
**Smoother Drive ** Electric motors provide quiet, vibration-free movement, especially noticeable during slow traffic commutes.
Government Benefits Some Indian states offer road tax rebates, lower registration fees or green number plates for hybrids.
Urban Driving Edge Perfect for Indian cities like Mumbai, Delhi or Bengaluru, where heavy traffic makes hybrids far more efficient than ICE cars.
Is a Hybrid Car Right for You? If you drive frequently in Indian cities, want better mileage and care about reducing your carbon footprint without fully relying on India’s still-developing EV charging infrastructure, a hybrid car is a smart choice. They offer the best of both worlds traditional power and electric efficiency.
The Future of Hybrid Cars While fully electric vehicles are growing in popularity, hybrids will play a major role in India’s transition to sustainable mobility. Automakers are investing in local assembly, more affordable hybrid models and battery innovations. Expect to see hybrids across more segments, from entry-level sedans to premium SUVs, all designed for Indian roads.
Conclusion
Hybrid cars are no longer niche, they are becoming the new normal in India. With their innovative features, significant fuel savings and eco-friendly advantages, hybrids offer a compelling alternative to ICE cars and a stepping stone toward a fully electric future.
Whether you are looking for savings at the fuel pump, lower emissions or a smoother drive, hybrid cars make a lot of sense on Indian roads, today and tomorrow.



